- Dyeing auxiliary for acrylic fibers: The introduction of highly acidic sulfonate groups improves absorption of cationic dyes.
- Acrylic Emulsions: Used to produce water-based paints and adhesives, emulsion sizes, or functional fine particles with excellent water resistance because it exhibits superior colloidal stability with a small amount of copolymerization and reduces the use of conventional emulsifiers.
- Water treatment agents: Used to modify acrylic acid scale inhibitors because copolymerization can provide thermal and chemical stability and dispersibility due to aromatic rings.
- Other: Detergents, dispersants, antistatic agents
- Home
- Product List
- SPINOMAR® NaSS
SPINOMAR® NaSS
Sulfonic acid monomer with excellent surface activity and polymerization
SPINOMAR® NaSS is a sulfonated vinyl monomer that combines superior surface activity and polymerization properties.
Copolymerization with acrylic and styrene monomers can impart cationic dyeing properties, thermal and chemical stability, dispersibility, and antistatic properties to a variety of polymers, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.

Main Uses


Feature
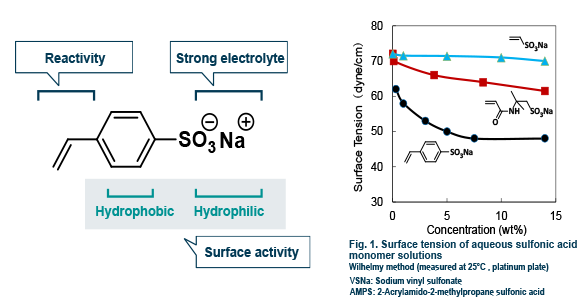
NaSS has an intramolecular sulfonate group and aromatic rings. Compared to other sulfonic acid monomers, it boasts a high surface activity (Fig. 1), polymerization, and heat resistance, as well as excellent storage stability and low toxicity (LD50 > 16 g/kg).
Since NaSS offers superior radical copolymerization with (meth)acrylate and styrene, it can be used for the above applications through emulsion or solution polymerization.
WO2014061357, "Purity and hue enhancement."
Related patents: JP5946094B, JP5930307B, US9505713B2, TWI579261B, CN1047365216B, MY-186412-A
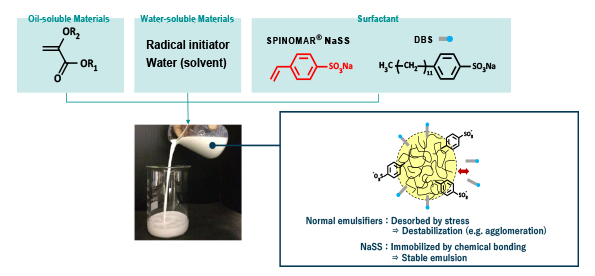
Example of emulsion polymerization and effect of NaSS introduction
NaSS is introduced to the surface of polymer particles via covalent bonds in emulsion polymerization; repulsion between sulfonate groups results in superior colloidal stability.
In addition, due to its compact structure, NaSS is a monomer that has fewer adverse effects on adhesion than common reactive emulsifiers.
Basic Information
| Chemical Name | Sodium p-Styrenesulfonate | Structural Formula | 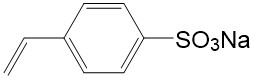 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 206.2 | CAS No. | 2695-37-6 |
| TSCA | Registered | EC No. | Registered |
General Properties
| Appearance | White to Pale Yellow Wet Powder | Boiling Point | No Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | No Data | Flash Point | Flame Resistancy |
| Specific Gravity and Density | Approximately 0.5 (Apparent Specific Gravity) |
Notes on Handling
- Use protective equipment to avoid direct contact with skin, hands, and eyes. In the event of contact with skin or hands, rinse with plenty of water. In case of eye contact, rinse eyes thoroughly and seek immediate medical attention.
- Oral toxicity (mouth): LD50 > 16 g/kg
- Store in a cool, dark place in tightly sealed containers to prevent drying, oxidation, and polymerization.
Packaging
25kg paper bag (with polyethylene inner bag)
